In this 2 part series, Jan Deichmohle adds his biosocial perspective to the ongoing nature/nurture conversation.
1. Abstract
This article shows that the female sex is biologically dominant. Sexual selection, procreation and a bias in perception of the sexes contribute to this dominance. Female dominance has been increased by all the “feminist waves.” The balance of society which had once unconsciously favoured women throughout history while also valuing men has been completely overthrown.
2. Introduction
Female choice being a determinant factor in the evolutionary cycle has severe consequences. It can create new species, and determine the course of evolution. It creates and forms the differences between the sexes1, as well as social structures like the family and culture. Charles Darwin and the Darwinian theory of evolution (circa 1858) laid the foundation of our understanding of natural selection and sexual selection. Recent studies on the subject have underscored its relevance and importance. See, for instance, Volume 1 “Culture and Sex2.”
“… sexual selection deals with variations between individuals, male and female, of the same species”
(Erika Lorraine Milam, “Looking for a Few Good Males, Female Choice” in Evolutionary Biology, pub 2010, p. 13)

«We assume that plumage dimorphism is a response to sexual selection and we assume that the males of plumage-dimorphic species experience stronger sexual selection pressures than males of monomorphic species. On Oahu, the extinction rate for dimorphic species, 59%, is significantly greater than for monomorphic species, 23%. On Tahiti, only 7% of the introduced dimorphic species have persisted compared to 22% for the introduced monomorphic species. …
Thus, the hypothesis that response to sexual selection increases the risk of extinction is supported for passerids and for the data set as a whole.» (Sexual Selection and the Risk of Extinction of Introduced Birds on Oceanic Islands, Denson K. McLain, Michael P. Moulton and Todd P. Redfearn, 1995)
The influence of biological female choice can push species into biological and cultural dead ends. These evolutionary tiger traps can lead to species extinction. For example, one specie of deer in the “Ice Age” was compelled to grow ever larger antlers in order to gain access to females. Eventually the species was unable to cope with the changes in the environment and consequently died out.3
“To sum up, the intensity of sexual selection in larger species in deer family put them in risk of extinction” (Saloume Bazyan, Sexual selection and extinction in deer, Uppsala Universitet, 2013)
The problem isn’t differences of the sexes. Different traits of the sexes cooperate and complete each other. They are useful within a culture. The problem is the pressure of sexual selection on men, becoming a driving force replacing natural adaption. This need not depend on the looks or sex differences; those traits were used to measure the degree of sexual selection. An even better method might be to determine the percentage of males, who could not procreate. The higher it is, the stronger the pressure of sexual selection.
«Fernandes and colleagues observed a possible result when studying fossil ostracods. … The researchers found a clear trend: Species, whose males had a lot of efforts for their features, got extinct 10 times as fast as other species. Sexual selection was pushing them into a dead end.»[1] (Neue Zürcher Zeitung 2018)
«These findings have led to the prediction that local extinction rates should be higher for speciespopulations with intense sexual selection. … we found that sexual selection increased risks of local extinction (dichromatic birds had on average a 23% higher local extinction rate than monochromatic species).» (Sexual selection affects local extinction and turnover in bird communities, Paul F. Doherty, Jr., Gabriele Sorci, et al; 5858–5862 PNAS May 13, 2003)
‘Sexual selection’ is a huge and complex subject so in this paper the reader is referred to Annex A where it is dealt with in greater detail.
Sexual selection and the certainty of motherhood give females easier access to procreation and make the female sex biologically dominant. Because children are the future, they get special protection and perception at an instinctive level, which then extends to females, who can be mothers. An innately favourable perception of women is the result. (For a discussion of female dominance in more detail and more evidence see Volume 1, “Kultur und Geschlecht”, English: “Culture and Sex”)
“This male-polarised/female-centering pattern is behind why males are regarded as advantaged and females disadvantaged… A pervasive misperception to the detriment of males would be expected to stem from the need to ‘police’ (to use the term as employed in biology) males to ensure they do not try to subvert the extent of sexual access they have by virtue of their ranking”
(The Origin of the Sexual Divide in the Genetic Filter Function: Male Disadvantage and Why It Is not Perceived, Steve Moxon, NEW MALE STUDIES: AN INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL ~ ISSN 1839-7816 ~ VOL. 1, ISSUE 3, 2012, PP. 96-124, © 2012 AUSTRALIAN INSTITUTE OF MALE HEALTH AND STUDIES.)
Males are regarded with a bias which becomes more prominent the lower his rank, and the less they should procreate because of their low rank.4 Mothers breast feeding babies have a direct special bond with the child and influence its mental development. All of this adds to the biological dominance of women. Let us look at the consequences.
In the animal-human continuum inter-sexual selection by the female of the specie can exclude the male from a fulfilled and contented life. The drives of procreation and the survival of genes are an inherent biological imperative. It has been strikingly laid bare that this holds among our own species – human beings.
Whatever the dreams or lifetime ambitions of a man might be – be it a specific beloved woman, establishing a world based on love and then to live within it, or a world of social and free love between the sexes – whatever that life’s dream may have been, it is often made impossible and their aspiration become destroyed by female choice, based on the power of sexual selection, which extends ever deeper into the realm of social life.
The male of almost all species must carry by far the greater burden of evolution. It is not the case that both women and men carry “fit” or “attractive” genes to procreate, resulting in only the “fit” or “attractive” genes prospering and surviving. No, virtually all fertile females procreate regardless of whether or not they carry “fit” or “attractive” genes; whereas only a proportion of males with genes regarded as attractive may procreate. A proportion of males pass the filtering process of sexual selection by carrying “attractive” genes. Most women who themselves carry “less-liked” or unattractive genes nevertheless still exclude men having the same less unattractive gene from procreation. Barred from access to a fulfilled love life, these men have their dreams of life destroyed by the discriminating choices made.
The “unattractive” genes however do not disappear quickly. “Unattractive” genes can be passed from a woman to a child down a long chain of generations. However, whenever the “unattractive” gene is passed to her son, he may well be discriminated against later in life, whereas if the “unattractive” gene is passed to a daughter, she will later in life most likely be able to still procreate. Were both women and men to face the same strict sexual selection rules, then those less unattractive genes would virtually disappear after one generation, speeding up evolution considerably. Or else, if neither of them would face sexual selection, then natural selection would steer a course towards a better adaption to the environment. In the current situation, the pressure to develop “attractive” genes may actually be higher than the pressure to develop “fit” genes.
Sobering as these statements are, they are nonetheless scientific facts, proven by genetic research.
“… The distribution of men’s mate value has a greater variance and more of a positive skew than the corresponding distribution for women. Females limit the reproductive success of males, and men compete with other men for access to women. ..Men have evolved to act as ‘filters’ for genetic material (Atmar 1991, Moxon 2008). ..By stretching men out in a dominance hierarchy, genetic material that enhances the lineage is retained, whilst deleterious genetic material is eliminated from the lineage. ..There is no dominance relationship (or competition) between men and women.”
Evolution by Martin Sewell, 31 March 2014, University of Cambridge
Examination of the graph5 below reveals that over the last 60,000 years, between four and five times as many women than men have procreated and left their genes within the human gene pool. We can safely assume, that the vast majority of women have procreated, whereas, at most, one man in four or five has procreated.
This is consistent with the biological fact of female choice, as stated by Darwin and confirmed by recent evolutionary biology. It is also consistent with feminist claims that women, given they have the choice, will select only 20 percent of men, while not wanting the other 80 percent. (see Volume 1 “Culture and Sex,” „Kultur und Geschlecht”)
An exception may have been the most recent few millennia, where human culture and what we now take to be “traditional” monogamous marriage may have resulted in a short period of less imbalance, while the underlying balance nevertheless still favoured women. There have been times of a huge imbalance, for instance, 8,000 years ago, when 17 times as many women procreated as men (see graphs below).
Figure 1: World reproductive population (in 000s) over the millenia
Left: Male population Right: Female population
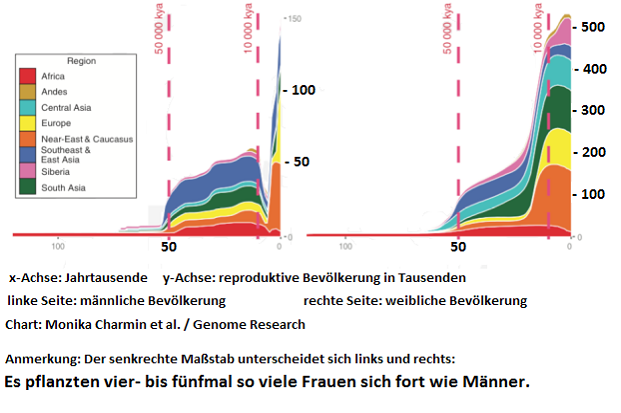
Four to five times as many women than men reproduced during the 60,000 years covered by the above graphs. The vertical (or Y) axis measures reproductive population in thousands, and the horizontal (or X) axis measures changes over thousands of years. NB. Please note: the vertical scale on the left differs from that on the right. Source: Monika Karmin et al. / Genome Research, Francie Deep, Mar 17, 2015, “8,000 Years Ago, 17 Women Reproduced for Every One Man”
Culture never “discriminated against women;” instead it was necessary for measures to be taken to reduce the degree of inhuman discrimination against men. That there was no oppression of women, but always an oppression of most men, has since been proven by science. Genetics is able to trace these specific facts back for more than 60,000 years, delivering exact proofs, while the feminist view is based on subjective perceptions, partisanship and myths, according to their own sources (see Volume 2 of “The Two Sexes”). Martin van Creveld has researched all the years of human history that can be covered in “The Privileged Sex.” The result was that women were always privileged.
In every culture throughout history women have been privileged and yet it was men who had to carry the burden to provide for the privileged status of women. Men were put into dangerous situations, including fighting for the protection of others and undertaking dangerous jobs or working anti-social hours, consistent with the “male filter” role of males. The life of women was much more protected, whereas men were expected to risk their lives for the benefit of others.
Whilst on the one hand, procreation was an almost certain option for healthy women, on the other hand a majority of men were denied procreation and thereby access, as genetics have proven (see graph below). This meant, a majority of men were effectively living a life of oppression. Therefore, claims of “discrimination against women” are as wholely contrary to the truth as they are wholely subjective. And yet regrettably all ‘feminist waves’ have built on this initial misconception and have actually exacerbated this elemental inequality.
The above figure 1 proves to what extent the burden of selection is mainly carried by men.
Under the pressure of inter-sexual selection (and in competition with other males) men must be successful in the eyes of women, sometimes according to unfathomable and often quickly changing fashions and patterns of female choice. The pace of change is especially rapid among humans: Some sources state the rate of change today is faster than at the time we split off from apes. Yesterday’s latest must-have fashions are today seen as a ridiculous and worthless aberations. Whoever is unfortunate to fall behind fashion, will be sifted out, discriminated against, and excluded. Fickle fashion decrees that what enthralled us yesterday, may be rejected and detested today.
With the power6 to decide whose genes live on and whose will die out firmly in the hands of women, the genetic pressure on men is huge. Men adapt much quicker than women because of this evolutionary pressure; they are the experimental laboratory (sometimes referred to as the “genetic filter”) of nature.
“male organisms evolve faster than their female counterparts” – ‘Live Science,’ Jeanna Bryner, Managing Editor, Nov 19th 2007.
It is undisputed that this faster change in males is linked to the pressure of sexual selection.
“The researchers suggest this … allows males to respond at the drop of a hat to the pressures of sexual selection.” – ‘Live Science,’ Jeanna Bryner, Managing Editor, Nov 19th 2007.
To enable fast adaption to the higher selection pressures men face, the array of variance between men is larger. Men are more likely to be found at the fringes of the statistical distribution. The male mutation rate is higher than the female. Both the very fit and the very unfit, the genius and the idiot, are more likely to be male than female.
“These have finally provided consistent results. Both Feingold (1992b) and Hedges and Novell (1995) have reported that … test score variances of males were generally larger than those of females. Feingold found that males were more variable than females on tests of quantitative reasoning, spatial visualisation, spelling, and general knowledge.” – John Archer & Barbara Lloyd, Sex and Gender, p. 187
A higher variance and mutation rate means that we would expect more variety of features. This enables some men to become “pop stars” of female choice discriminating against a majority of men.
While a large variance enhances the chance of some men fitting in to the newer demands by sexual selection, others fail completely. Statistically, women are more likely found in the middle, the average, whereas men are more often found at the fringes.
This also results from the aforementioned biological fact, that men carry the burden of evolution.7 (see also Annex A, “Sexual Selection”) The one-sided sexual selection is unjust and contradicting the idea of equality. Feminism has declared war on all ‘facts of life’ that it does not like, and has tried (and at times has succeeded) in eradicating them, while protecting all their favoured ‘facts of life’ as sacrosanct, and further strengthening their perspective. There is neither balance nor justice in such a process.
Female choice steers evolution away from ‘adaption to environment’ by natural selection. If we assume a situation without sexual selection by either sex, natural selection would enhance adaptation to fitness and environment.
Female choice is the most momentous, the most consequential of all choices. Men are not given this kind of choice by nature. Even in other domains men have never had a comparably momentous or consequential set of choices. Male-specific attributes are therefore needed if men are to avoid being discriminated against, and even more to have a secondary choice of their own among those women who already selected him by their female primary choice.
To avoid discrimination or to have a secondary choice, men need good reputation, and a sufficient degree of power and wealth. Male domains are also required, for the males as well as for the sake of female choice: females need and ‘police’8 the male hierarchy, because it is important for their choice.
(Selection – as we use the term here – doesn’t mean there’s a relationship or love. It means that she is willing to accept an approach by all the men she selected. Usually it is the male who is supposed to approach the female, but it is the female selection process which actually dictates whether his approach is allowed or not. Our misperception is to believe the active male would make the decision, whereas it has been clearly observed by scientists, that among humans the passive female makes the decision. A groupie might select virtually all the famous male rock stars and is open to accepting virtually all approaches made by these rock stars – see the “boy group” example below.)
These same qualities and structures men need to avoid being rejected by female choice, they also need to avoid the innate bias in perception against males of low rank. The perception bias has the same reason: The lower their rank, the less access to procreation males should have. Low rank males are supposed not to procreate. Were we to perceive them favourably and with sympathy, they could ask for help and love and thus thwart the whole system of evolution. Therefore, evolution created a protection mechanism, a biased perception resulting in biased treatment. Women and children are preferred by perception to protect and support the future of the tribe. To avoid an unfair perception, men need a positive ‘edge’ in the form of high rank and reputation. Becoming aware of this usually unconscious mechanism also helps in the overcoming of it and achieving a more balanced perception.
Some femininst literature sources put the figure of men who are winners of female choice at 20% (see Volume 1 and also the figure shown above, which both support that number). Only those winners in the “sexual selection stakes / race” have a fair access to the gene pool by their secondary choice. The remaining male population (the majority of males) face access limited on a sliding scale from mediocre to very poor or none at all.
Because there are many more heterosexual women than men matching their high and discriminating demands, there are often large numbers of male losers whose life is constricted and afflicted, but also some winners, which more women want, than there a men that they want.
The losers are shown in figure 1 above, the winners will be discussed below, see the “boy group” example.
Such pressures (deriving from inter-sexual selection and resulting competition for rank) inevitably then become ‘social’ pressure, resulting in high male suicide rates, as figure 2 below for Canada (by age) illustrates. The increase over the age range from 10 years old to 30 years old is also typical of the US and UK.
Figure 2: Suicide Rates By Age and Sex in Canada 1998
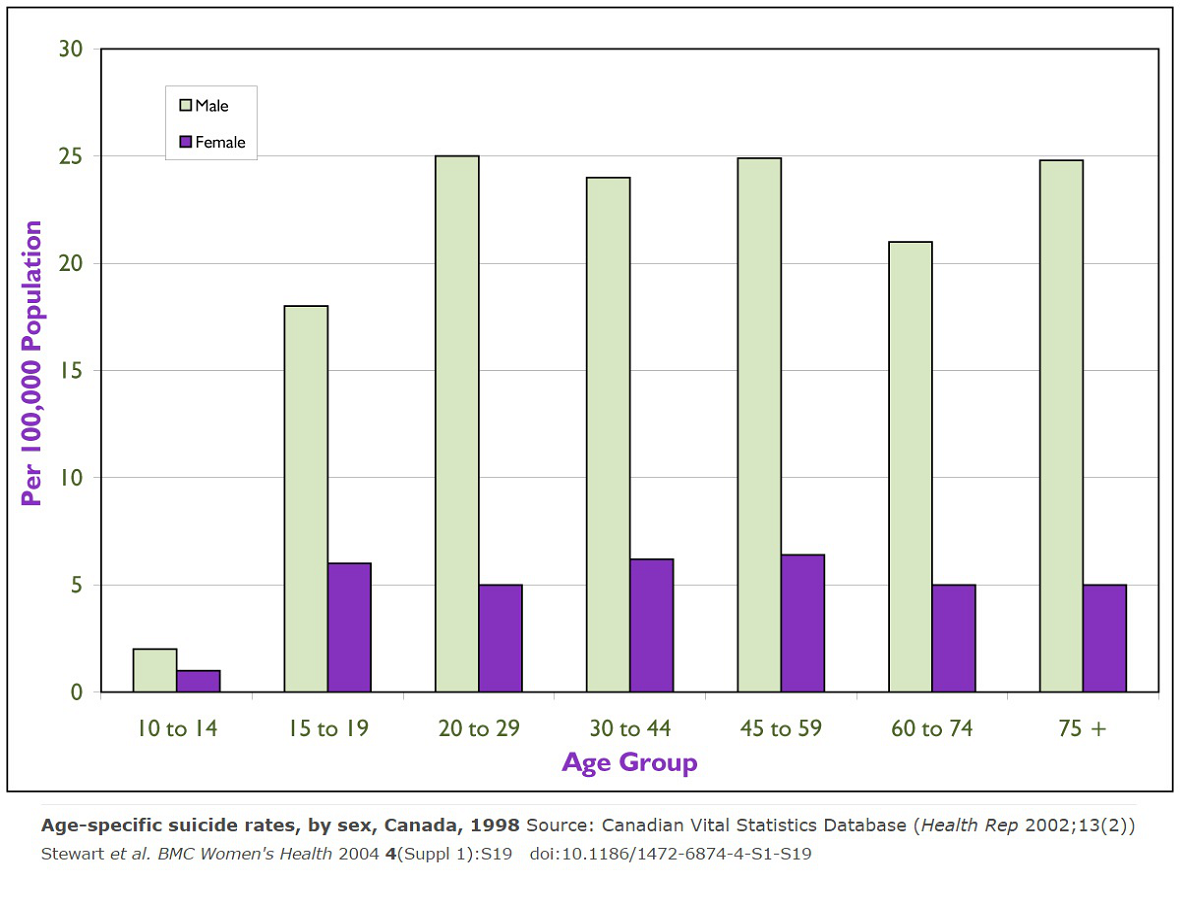
“. . . From the data available (and shown here in graphs) the ‘critical years’ begin at 11 and end at 19 years of age. Throughout this period boys are undergoing many internal developmental and hormonal changes to their bodies and are having to adapt to new roles expected of them by society This is particularly true of the 11-14 year old category when boys are passing through various biological stages of adolescence that may radically alter their behaviour or responses from just a few years earlier. There is not one clear single event such as menstruation as for females
The next critical phase, whilst still linked to the changes just mentioned, is at around 15 and 16 years of age and may be related to stress induced by exam pressure.This could be compounded by peer pressure as girls begin to figure more largely in boy’s priorities. Exam failure or even fear of exam failure can be the trigger for hasty action by some young people. Getting or keeping a job can have a similar effect. Failure to get a job interview can lead to self-doubt and worth loss of self-esteem. The momentum is still upward when A levels and university hove into view at age 18 and 19.”
From the viewpoint of biology, the underlying pressures are 1. female choice (inter-sexual selection), 2. the social pressure of peer group, education and exams, or work, which are all forms of intra-sexual selection within the male dominance hierarchy. The rise in suicides of men during puberty and adulthood is consistent with the view presented in this article.
Figure 3: Suicides of young men (1996) (England & Wales only)
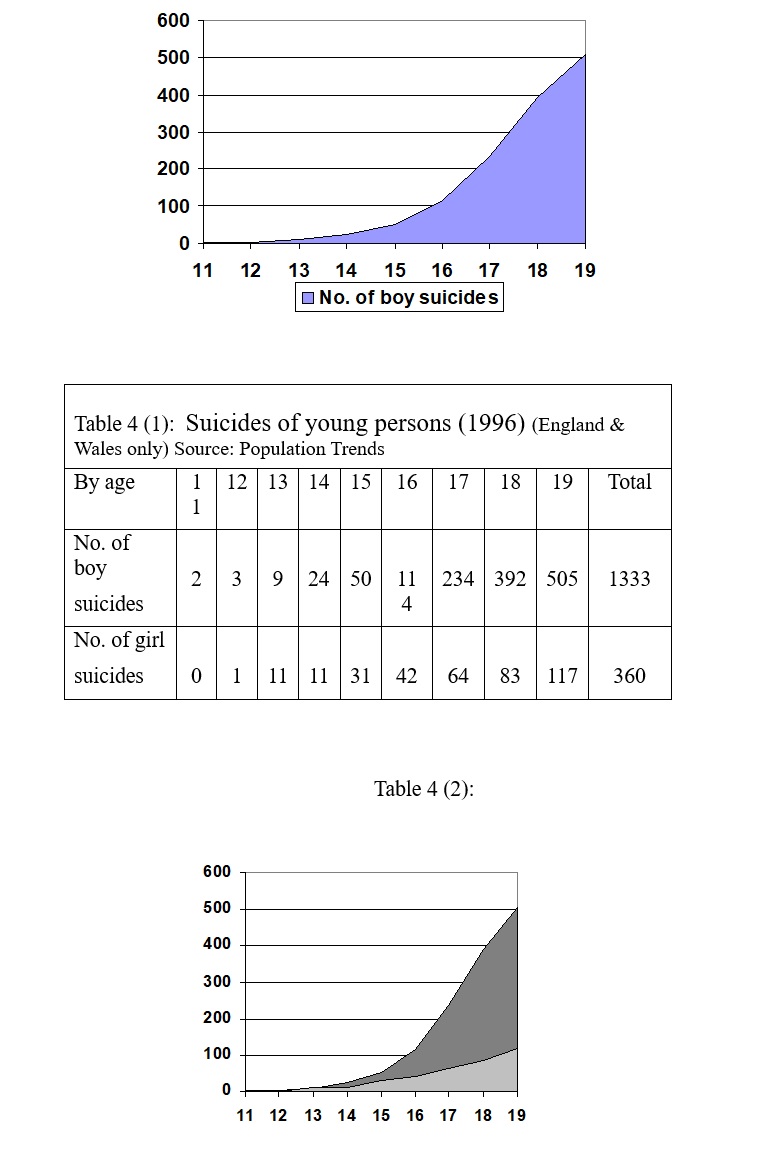
3. Applying the Biological Facts to Society
 When we examine the phenomenon of “boy bands” for example, the first and most revealing model is probably ‘The Beatles.’
When we examine the phenomenon of “boy bands” for example, the first and most revealing model is probably ‘The Beatles.’
The members of the band were drawn from a pool of average adolescents, same-aged, pimply boys from the local neighbourhood. The average boy may be inexperienced and clumsy, and without their fame or skills, he will most likely be pre-destined to be discriminated against, mocked or even treated unkindly. There are millions of this kind of average young male. The first Beatles movie “A Hard Day’s Night” shows a scene, where a woman scoffs at a Beatle greeting her, because she didn’t recognize him (as a celebrity, and now a high-ranked male that Beatle-mania bestowed) in the old clothes he was wearing to avoid publicity, (after having been chased by screaming girls shortly before).
At the same time, teenage girls were quite prepared, for example, to overrun police barriers, cordoned off areas, cause traffic jams whenever the “Fab Four” (the Beatles) arrived in their town for a concert, just to be near their idols; their heroes. Concurrently the ‘phenomenon of the groupie’ associated with various rock bands began to emerge at this time. Both are a form of strong sexual selection.9
By contrast, the average boy from the neighbourhood was still perceived as clumsy due to his lack of experience, lack of fame, talent or rank, and thus finds himself discriminated against. Because there are many more “girls and boys from the neighbourhood” than there are Beatles, the selected few men (of the band) now have a (social) secondary choice among the women who already selected them.
Many teenage girls might fantasise that her favourite, or otherwise any member in the band she adores, would chose her among all the other screaming girls – and she would often long to sleep with him. So even male pop stars who epitomise the exercise of power and wealth are in fact still selected by female choice. As previously stated, it is a fact of biology that male power and dominance is an exclusively male issue which is sorted out only between men, not between men and women. There is no male dominance over females in biology. Feminists misunderstood such facts of life and interpreted them the wrong way around. Destroying male power does not result in more ‘equality,’ but in sharply increased imbalance instead.10 The feminist cultural revolution spread across society was based on the misunderstanding of the most basic and important facts of life.
For more details and proofs, see for instance Volume 111, “Culture and Sex” – this book also proves the importance of cultural complementing structures between the sexes, a topic probably even more misunderstood and important than the topic of this paper.
Former members of the Beatles have told of women, who were proud of having conceived as the result of a “groupie encounter” with a Beatle, and to have then given birth to a “little Beatle” as her child. (some of them didn’t ask for money)
In former times a similar attitude prevailed with sexual liasions with monarchs, for instance, ‘August the Strong’ of Sachsen is reported to have fathered 100 children. Often, the attraction of young women is directed towards those that exhibit negative celebrity status, those famed for anti-social behaviour; even incarcerated famous male murderers are overwhelmed by female fan post and are favoured by some getting married while behind bars, even when awaiting execution. What does this mean for the human gene pool, and who is responsable for it?
Meanwhile, our typical boy from the neighbourhood has considerable problems. If he tries to talk about being rejected, he faces denigration. The matter will be portrayed as “adolescent problems12.”.
But is is not only boys that face discrimination, and the denigration, should they try to talk about it. Young men and mature men face the same barriers. So both problems have nothing to do with “adolescence.” Both problems know no age barrier, since men of all ages encounter discrimination by sexual selection and tendencious perception, which extends to social life in general, even to areas of life not linked to the evolutionary origin of this prejudice. One among several reasons is, that women and children are permitted to complain, whereas men may not. Once again, the evolutionary sense of this taboo is to stop low-ranked males (as the clumsy adolescent still is) from getting “undue access” by complaining and begging for what sexual selection by rank denies him.13 Yet the resulting prejudice in perception and access extends to social life in general.
Female choice harms not only the majority of males (by excluding and thereby unnecessarily turning them into losers), but also creates a secondary choice of the small group of male winners, resulting in a secondary competition among women. Even though this results in giving a social secondary choice to a few male winners (at the expense of a majority of losers), the biological power of primary choice is female and contributes to making the female sex dominant.
Even though it may at first glance appear paradoxical to the reader, strong female choice creates stiff competition between women for the few males which the females select. It results in women doing a lot to feel attractive and to outshine their female competitors.
Often, people do not even realise the biological machinery at work. Women frequently state, they would face difficulties finding a good man themselves, and that they would find it hard to get the man they wanted (‘Mr. Right’). Our perception obscures the biological facts. Women’s competition for men only results from having previously discriminated against a large majority of men. Unthinkingly, we completely misunderstand the situation if we don’t keep the biological facts in mind: Primary choice is female only and givcn by biology. Men don’t have a primary choice given by biology and face heavy competition in male hierarchies to attain the required rank caused by the pressure of female choice.14 However, if women discriminate too much, a few male winners will have a social secondary choice, and women face a secondary competition within their own ranks.
A scientific study links this secondary competition to the spread of female discontent with their own body, and eating disorders. (see Volume 1) Because many women are competing for a few selected men, they try to outdo each other by having a more ‘perfect body’ than other women and tend to be dissatisfied with their own body (the so-called ‘body image’ dilemma). Trying to be slim which is currently in fashion circles, they are more prone to eating disorders and psychological ill health problems. In traditional cultures such discontent and psychological disorders are rare, because those traditional cultures reduce the pressure of female choice on both sexes. Marriage and relationships are not left to only inter-sexual selection in such cultures, thereby reducing its pressures.
Hence female power of choice by inter-sexual selection harms most men; (and in the process) also the selecting women themselves, the society and the gene pool, in which genes and characteristics of murderers and anti-social thugs are spread, because their carriers are preferred by some women.
Female choice is the core of all sexual discrimination; it is 750 millions of years old – in fact, it is as old as the existence of both sexes. Sexual discrimination has always been done by women, for biological reasons (even if we are not aware of it).
What “feminist waves” subjectively assumed, inspired by feelings15, was absurd nonsense contradicting the biological “facts of life.” Woman do discriminate, since they are females and are forever searching for their Prince; whereas men are much less “picky” for biological reasons. Men can get excluded from access – (from family, sexual fulfilment, and even socially in many ways by their rank) – and have to work or struggle for that access, but not women. (As a proverb tells: “Men marry down, but women marry up.”)
—- to be continued next week —-
Source, Thanks And Further Readings
Robert Whiston has given some help in translating this article to English.
The above is an excerpt from my upcoming book which currently has the working title “Censored,” Volume 4 of “The Two Sexes.” („Zensiert”, Band 4 der Reihe „Die beiden Geschlechter”) The important facts and fundamental premise are laid out in Volume 1, “Culture and Sex. Feminism: Big Mistake – Severe Consequences” („Kultur und Geschlecht”, Band 1 der Reihe „Die beiden Geschlechter”) and Volume 2, entitled “Refutation of Feminist Ideolgy: The War On Men, Nature and Culture” of a series headed “The Two Sexes.” („Ideologiekritik am Feminismus: Krieg gegen Mann, Natur und Kultur”, Band 2 der Reihe „Die beiden Geschlechter”)
A more detailed view on the impact of current feminism on cultures is given in Volume 3, „Die Genderung der Welt: Wie Feminismus weltweit Kulturen zerstört”. (“Gender-Mainstreaming the World: How Feminism Destroys the Cultures of the World”)
Apart from the topic of selection which this article dealt with, there are other important topics to be dealt with, where feminism has created lots of damage to human life, culture and society. Traditional culture, a common trait of all hominides, is based on the sexes complementing each other, a differentiation of labour, and an exchange of work, work results and responsibilities. Exchange itself (i.e. interaction) may be more important than what is exchanged. More than just of practical benefit, this mutual care is also symbolic and important for the development of feelings, responsibility and bonds in general, and it is the basis for cultural structures which are as important as (and comparable to) language. This is proven and explained in Volume 1 of “The Two Sexes.”
Annex A
Evolution is a biological process driven by selection. Research into evolutionary biology demonstrates the male sex serves as a filter for “deleterious genes”. In contrast, almost all the females of a specie procreate under normal conditions, or could procreate wihen they want to. The exceptions are fatal diseases or infertility caused by genes. Males on the other hand are ‘filtered’ in many ways. The child born by a mother is always hers. Fatherhood is not certain.
Males are put into (find themsleves in) a single sex hierarchy of dominance which serves as basis for female choice. Males are required to obtain a high rank to gain access to females for procreation. This holds as true for humans as it does for those other animals closely related to our specie. Males who do not have superior, ie bad genes, are likely to fail in competition with other males and be excluded from procreation.
Males have to toil and to seek to achieve success. Whereas a culture, or even a sub-culture may create a large variety of different scales of dominance, the rigid system of male hierarchical dominance is always present. Females are not subjected to such a hierarchy (NB. Dominance is strictly only between men. The feminist concept of male dominance over women is a fallacy, and by biology is proven to be a false premise. Neither for animals, nor for humans, does a dominance of men over women exist. It’s a false perception contradicting facts of biology.)
Competition between men is called “intra-sexual selection”. Men alone carry this additional burden of intra-sexual selection before competing for females. Women do not have such a hierarchy, nor are they ever part of the male. Biological mechanisms punish men competeting with women by destroying their status and reputation.
If, as is done today, men are mixed with women in the workplace then work tends to cease to be a means of determining male status and dominance. Thwarted this innate competition strictly limited between men will seek out different areas to express itself. The consequence is that not success at work, but success at some lesser important activity will determine who can procreate or not. This will results in poorer selection standards because ‘selection of the fittest’ has been debased and instead society conforms to some random fashion. It also discourages boys and men to learn and study.
Men are exposed to dangerous situations and may die in the process. That is “natural selection” in action. Women are not meant to be put into such situations. As they are never part of the male hierarchy of dominance, they don’t compete for male status. They’re not requested do dangerous work or fight in wars. Clearly, therefore, men carry more of the burden of natural selection than do women.
The third selection of the evolution process is called “inter-sexual selection”. It is the domain of female choice and female dominance already mentioned. However, once again, the burden is actually carried by men. We will see that an overly restrictive female selection can ironically create a secondary competition between women for the few selected males, and a secondary choice of few selected males at the cost of the majority. This overacting doesn’t contradict our statement; instead, it supports the argument.
References
1«Sexual Selection and the Evolution of Human Sex Differences
Chapter 7 Developmental Sex Differences
Is sexual selection related to differences in the physical, social, and psychological development of boys and girls? The goal of this chapter is to address this question by examining the pattern of sex differences across a variety of domains and by relating these sex differences to adult sex differences in the nature of intrasexual competition, parental investment, and so on. Developmental sex differences in the pattern of physical development, infancy, play patterns, social development, and parenting influences are described in the respective sections below. The pattern that emerges across these sections is consistent with the view that many developmental sex differences are indeed related to sexual selection and involve a largely self-directed preparation for engaging in the reproductive activities described in Chapter 4 and Chapter 5.» (Male, Female; The Evolution of Human Sex Differences by David C. Geary)
2 Jan Deichmohle, “Kultur und Geschlecht”, Band 1 der Reihe „Die beiden Geschlechter” English: “Culture and Sex,” series “The Two Sexes”
3 Theoretical models, such as a Fisherian runaway process, suggest that evolution of preference and preferred phenotypes may drive each other in ever increasing speed. Though there are different models debated, this is a possible scenario. Even without a runaway process, there is a risk, for instance when the environment changes and the prefered phenotypes (antlers) become an obstacle. Sexual selection is the most likely explanation of the extinction of several species.
4 Would we perceive low-ranked males with more empathy, they could get more access to procreation than they are supposed to get (in the view of evolution). Those who are not supposed to get access to procreation matter less for the tribe, even socially, and face social discrimination as well, by men and women. Even their death has less importance to the tribe, as their genes won’t live on anyway. This may be the basis for injustice, if we don’t
realize and thereby overcome the bias. Those low ranked males do the work and take risks without getting reward.
5 see Figure 1: World reproductive population
6 We may not be aware of it. Matters of rank and selection often happen unconsciously.
7 Apart from the pressure of sexual selection, genetical reasons add to the burden. Men have one X and one Y chromosome, exposing any defect in it, whereas in females, the second X chromosome may cover the effect of a defect. Furthermore:
“In many plant and animal taxa mutation rates are higher in males than in females.” (Evolutionary Ecology (2006) 20: 159–172,
Springer 2006, CHRISTIAN SOM1,2 and HEINZ-ULRICH REYER, Research article.
<br>
8 As Steve Moxon noted, a majority of males having a lower rank has rather an interest of overthrowing the male hierarchy, because it is of disadvantage for them. Or else, if they can’t overthrow it to reach the top area themselves, they try to cheat and act as higher-ranked than they really are. Both high-ranked males and females co-operate in keeping the hierarchy order stable. According to Moxon, females have even more of an interest in policing the male hierarchy orders than males, because they depend on it for sexual selection.
9 Groupie (or gruppie) – a young woman who regularly follows a pop group or other celebrity, especially in the hope of having a sexual relationship with them. Some have followed many a or any famous group. In contrast, a fan just likes the music.
10 We established a biological dominance by the female. The dominance is based on at least the following: Sexual selection, giving birth to children, inborn bias of perception favouring women (potential mothers), and another innate bias discriminating men (who should not easily procreate). Given the biological dominance of women, men need male powers to reach equilibrance. Natural behaviour and traditional culture provided some balance, though women were always privileged. These social male powers are much more fragile than inborn female dominance. That’s why men have to work hard to achieve it, and revolutions, or feminism, could overthrow them. That many assumed male dominance in the past is a misconception. Male power is a staging, a show, and a necessary one. In spite of all praise of “male power” you may find in past eras, this was just a surface needed to counterbalance female dominance. It was not real dominance, excluded by biology. Rather, it is a show, and this show is needed for balance.
11 „Kultur und Gechlecht” (“Culture and Sex”), Volume 1 of „Die beiden Geschlechter” (“The Two Sexes”)
12 Derogatory remarks and the general denigration of such problems have been documented in my other book series „Die Wahlmacht der Frau” (“The Power of Female Choice”). Not only the men get denigrated, even the problems themselves, because society doesn’t want to become aware of the problems and excludes them from consciousness.
13 There are two opposed remedies for this situation: The one is to easen access to lift the pressure. The traditional is safer, more solid and effective: Both sexes, boys and girls alike, are requested to grow up responsibly within their sex groups, which have a structural bond by complementing and exchange (a kind of barter on a symbolic level). There are cultural mutual responsibilities, „structures of complementing”. Such structures create bonds. They are binding forces opposing exclusion, which can result from selection. (see „Kultur und Geschlecht” for a discussion.)
14 Feminist complaints about male competition got cause and consequence the wrong way around, too. It is women who need to change and discriminate men less, if they want less competition of men.
15 By basing their view on feelings and subjectivity, feminists were hit by the evolutionary “bias of perception” trap.